Choosing the most suitable heat source for your industrial hot air dehydrator is a crucial decision impacting operating costs, efficiency, and environmental impact. This guide explores three common heat sources available for your dehydrator
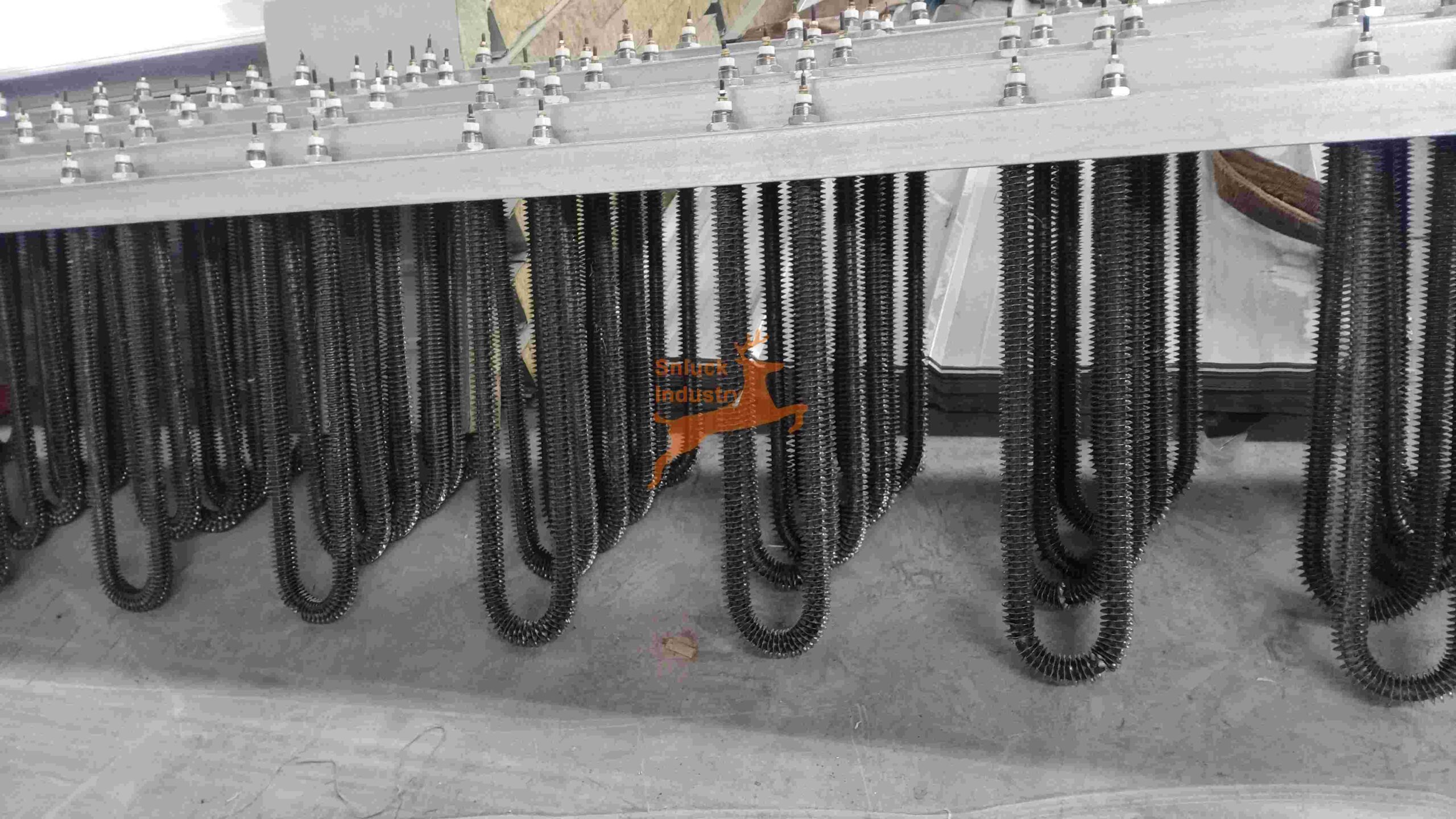
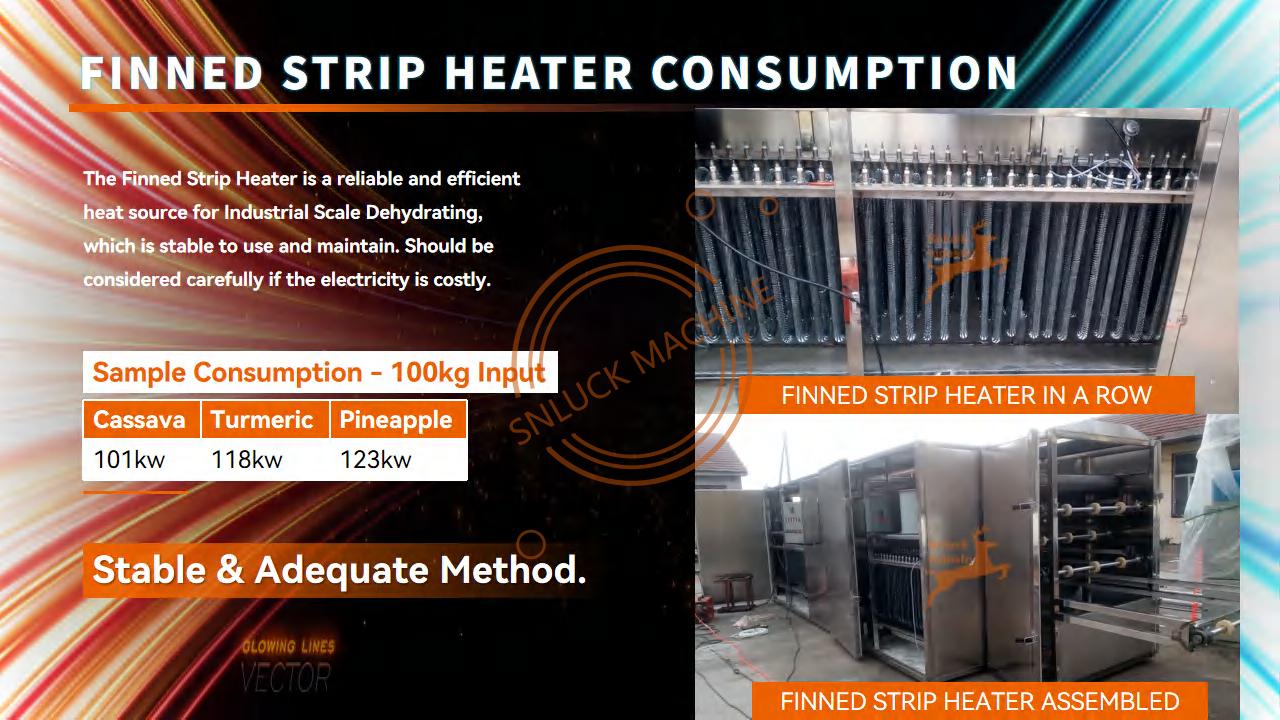
- Function: This traditional heating method utilizes electric finned wires to convert electrical energy directly into heat. The heated air is then circulated within the dehydrator chamber to dry your product.
- Advantages:
- Simple and Reliable: Mature technology with readily available components, offering a familiar and easy-to-maintain heat source.
- Precise Control: Allows for accurate temperature control within the dehydrator chamber.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher Operating Costs: Electricity can be a more expensive energy source compared to some alternatives.
- Environmental Impact: Reliance on electricity generation methods can contribute to a higher carbon footprint.
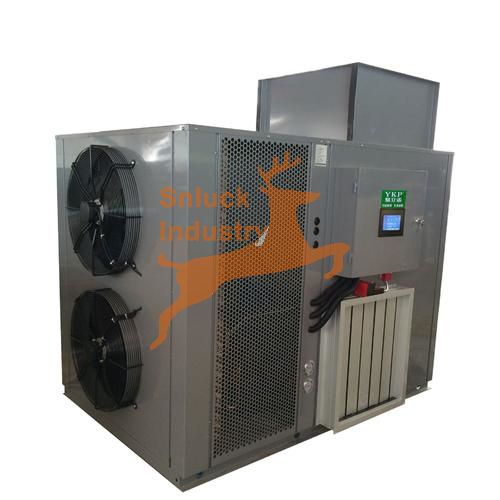

- Function: Electric heat pumps utilize a unique technology to transfer existing heat from a cooler environment (ambient air or a secondary source) to the dehydrator chamber at a higher temperature.
- Advantages:
- Energy Efficiency: Heat pumps can significantly reduce energy consumption compared to traditional electric heating methods.
- Environmentally Friendly: Lower energy usage translates to a smaller carbon footprint.
- Disadvantages:
- Higher Initial Investment: Heat pumps may have a higher upfront cost compared to electric finned wire heating.
- Performance Dependence: Efficiency can be influenced by ambient temperature conditions.
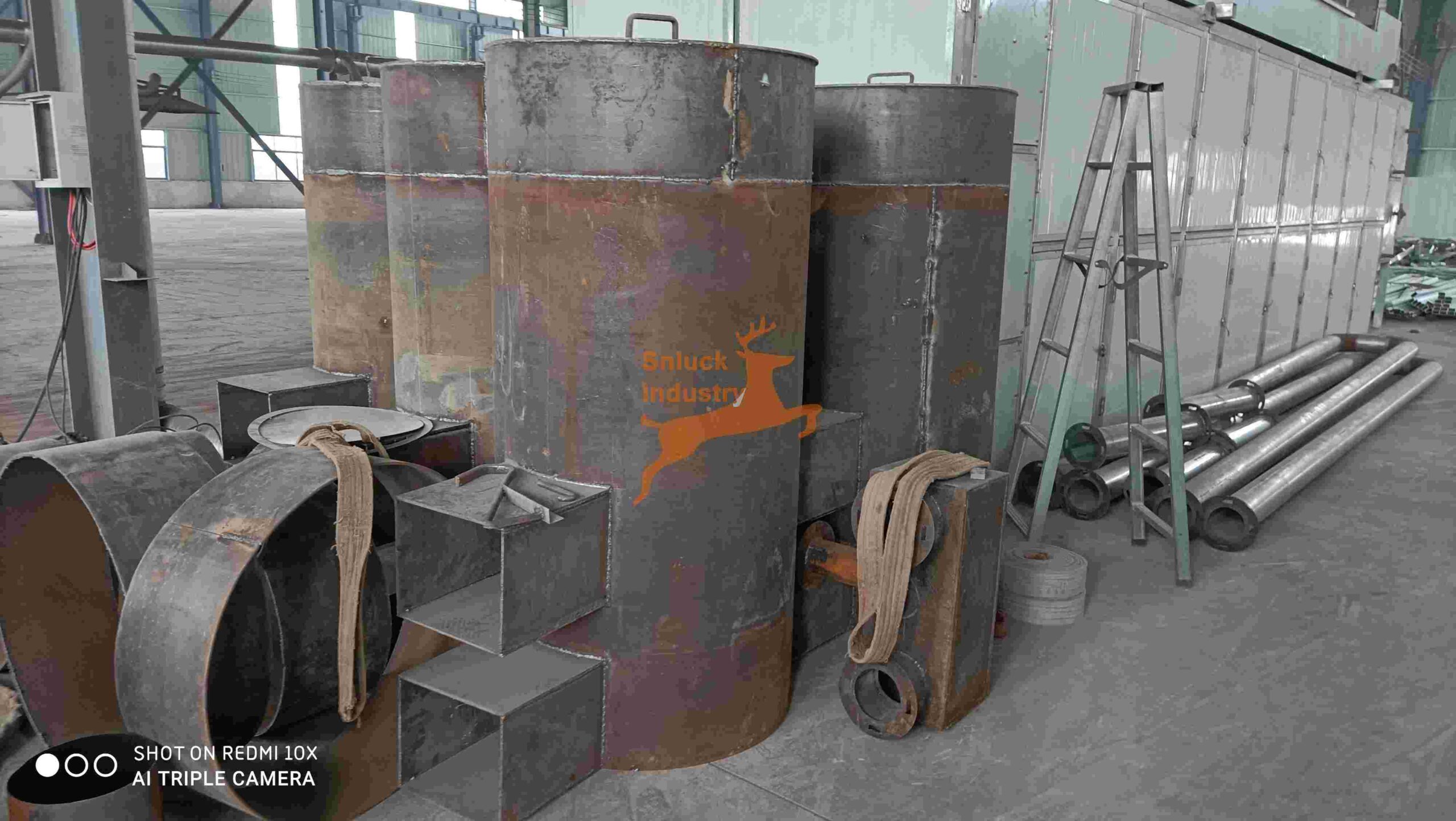

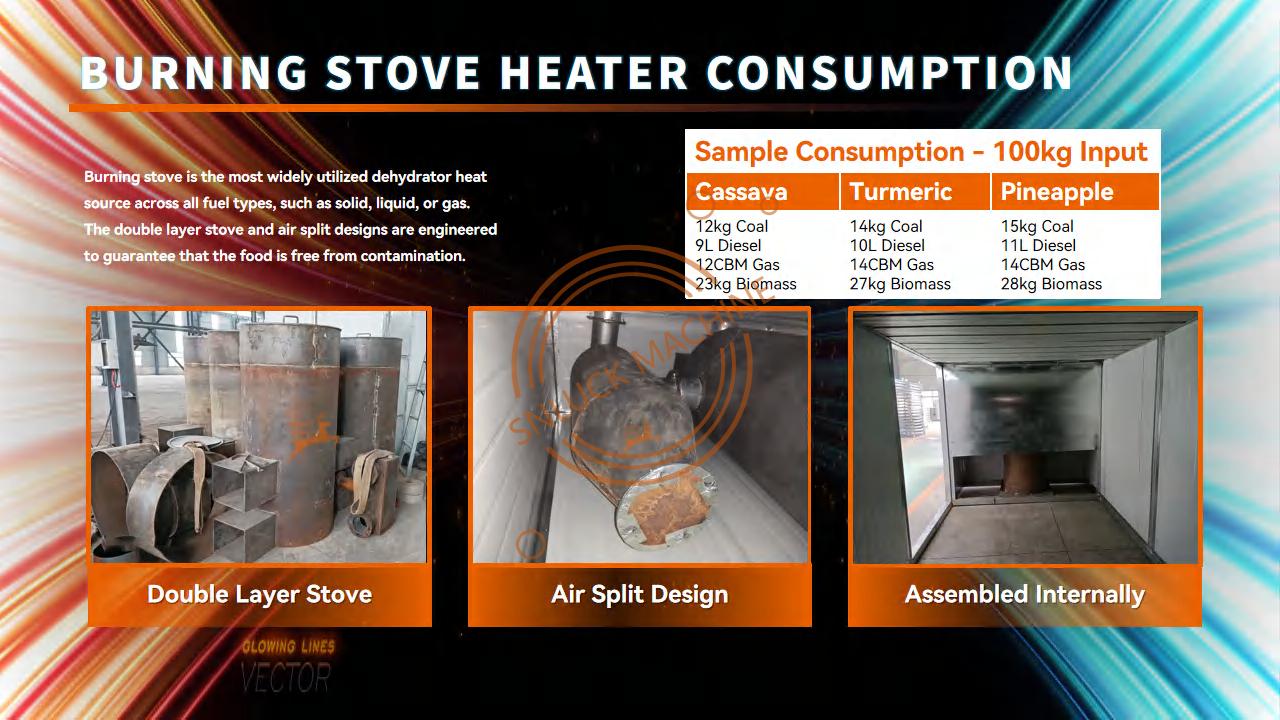
- Function: Combustion furnaces burn various fuels, such as natural gas, propane, or biomass, to generate heat. This heat is then transferred to the dehydrator chamber to dry your product.
- Advantages:
- Potentially Lower Operating Costs: Depending on fuel prices and availability, combustion furnaces can offer a cost-effective heating solution.
- Fuel Flexibility: The ability to utilize different fuels provides flexibility based on availability and pricing.
- Disadvantages:
- Emissions and Regulations: Combustion generates emissions that may require additional equipment or permits to comply with environmental regulations.
- Maintenance Requirements: Combustion furnaces generally require more frequent maintenance compared to electric options.

- Energy Costs in Your Region: Evaluate current and projected energy prices for electricity and available fuels.
- Production Volume and Dehydration Needs: Higher volume operations may benefit from the efficiency of heat pumps, while smaller-scale applications might find electric finned wire heating suitable.
- Environmental Impact: If sustainability is a priority, consider the environmental impact of different heat sources.
- Regulations and Permits: Research any local regulations or permitting requirements associated with specific fuel-burning furnaces.
By carefully evaluating these factors and discussing your specific needs with our team, we can help you select the most cost-effective and environmentally responsible heat source for your industrial hot air dehydrator.
| Feature | Electric Finned Wire Heating | Electric Heat Pump | Combustion Energy Furnace (Multiple Fuel) |
| Function | Converts electricity directly into heat | Transfers existing heat to a higher temperature | Burns fuel (natural gas, propane, biomass) to generate heat |
| Advantages | Simple & reliable, precise control | Energy efficient, environmentally friendly | Potentially lower operating costs, fuel flexibility |
| Disadvantages | Higher operating costs, environmental impact | Higher initial investment, performance dependence on ambient temperature | Emissions & regulations, maintenance requirements |
| Suitability | – Ideal for applications prioritizing simple and reliable operation – Good for facilities with readily available and affordable electricity | – Ideal for prioritizing energy efficiency and environmental impact – May require moderate initial investment budget | – Well-suited for operations with access to cost-effective fuels – Consider if environmental regulations are not overly stringent |
| Cost | Lower initial investment, but higher operating costs | Higher initial investment, but lower operating costs | Potentially lower operating costs depending on fuel prices, but higher maintenance costs |
| Maintenance | Relatively low maintenance requirements | Regular maintenance required | Regular maintenance required, potential for additional emission control maintenance |
| Environmental Impact | Relies on electricity generation methods which can have a higher carbon footprint | Lower carbon footprint due to lower energy consumption | Generates emissions that may require additional equipment or permits |